
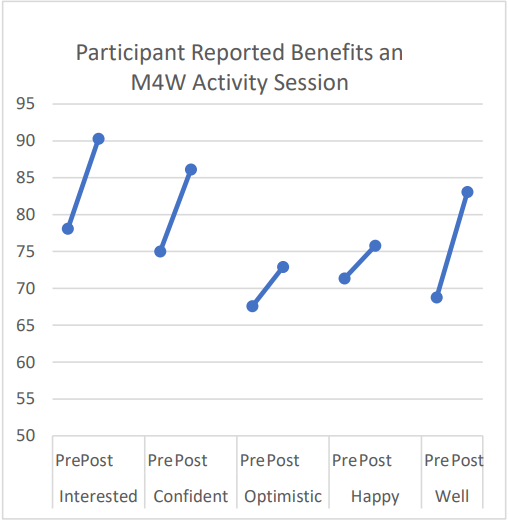
The UK Government and World Health Organization recognises that music and the arts can be instrumental in helping to address complex problems and to maintaining the good health and wellbeing of the nation.
It is known, for example, that singing can help to:
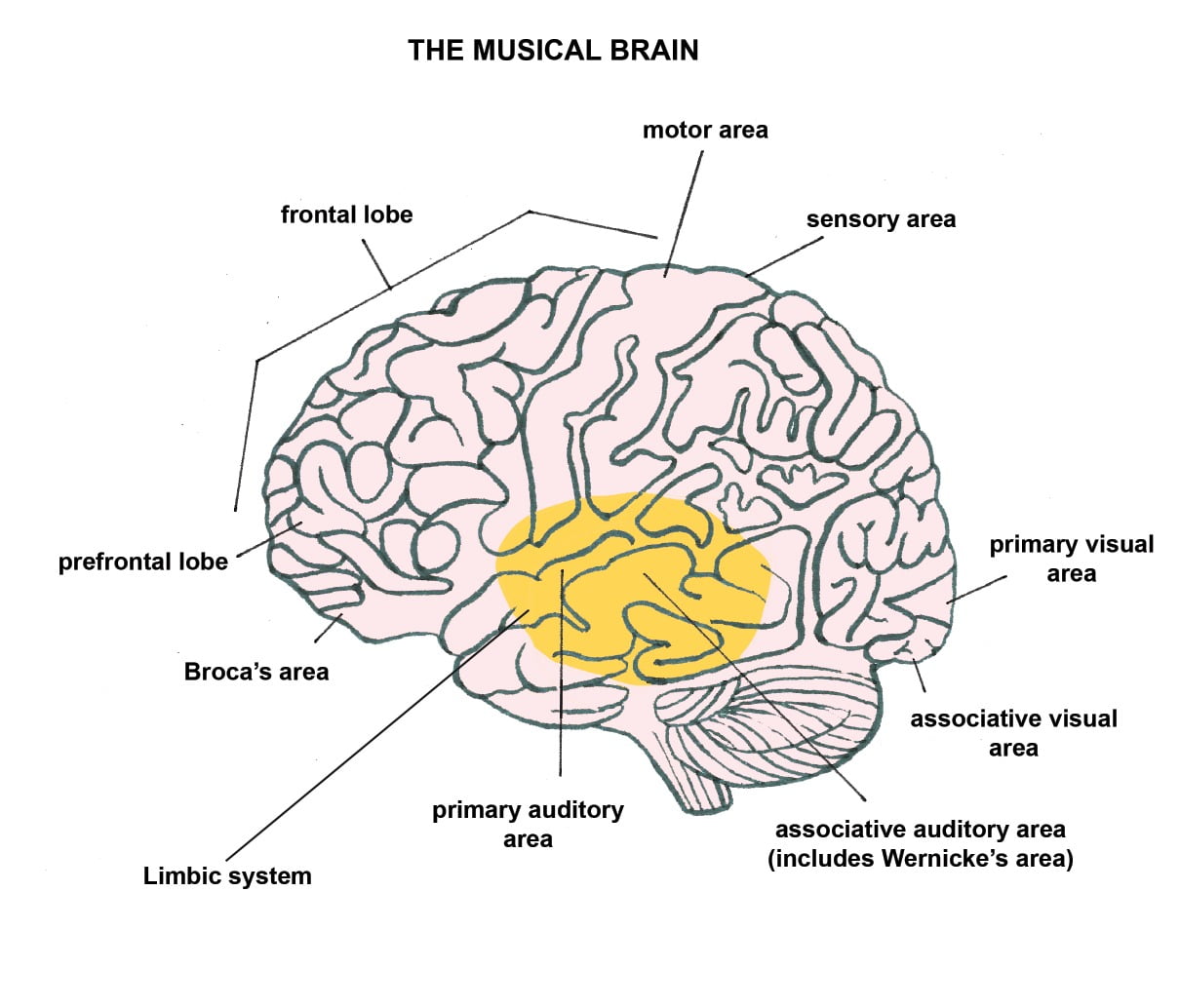
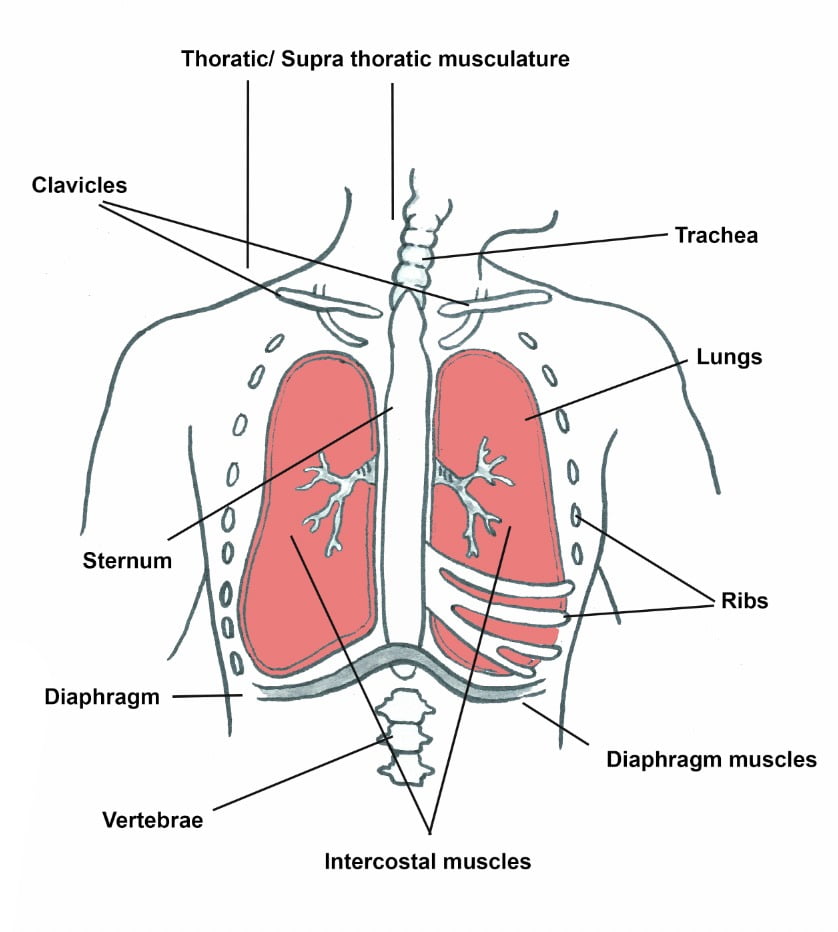
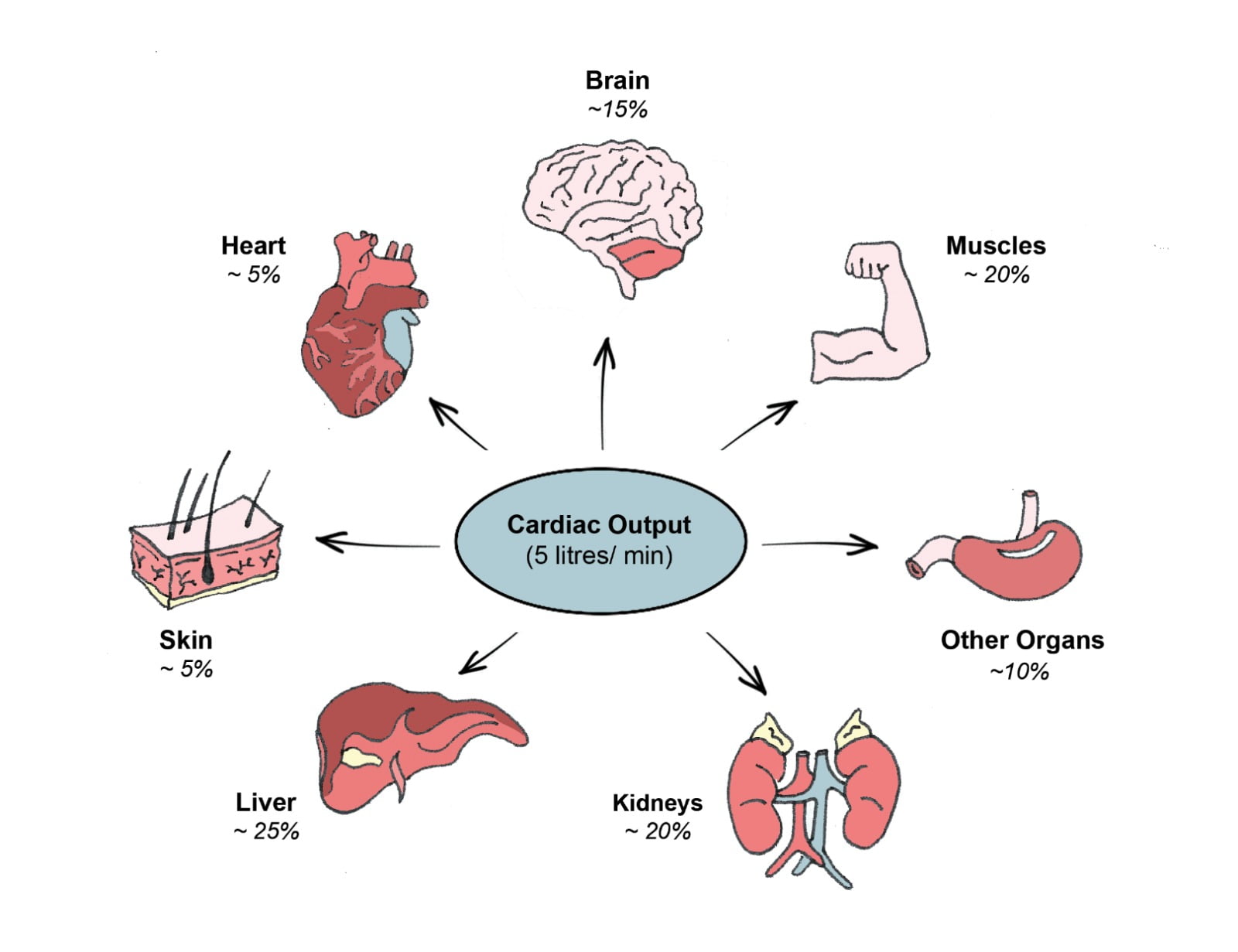
When we engage in music, many areas of the brain are stimulated at once.
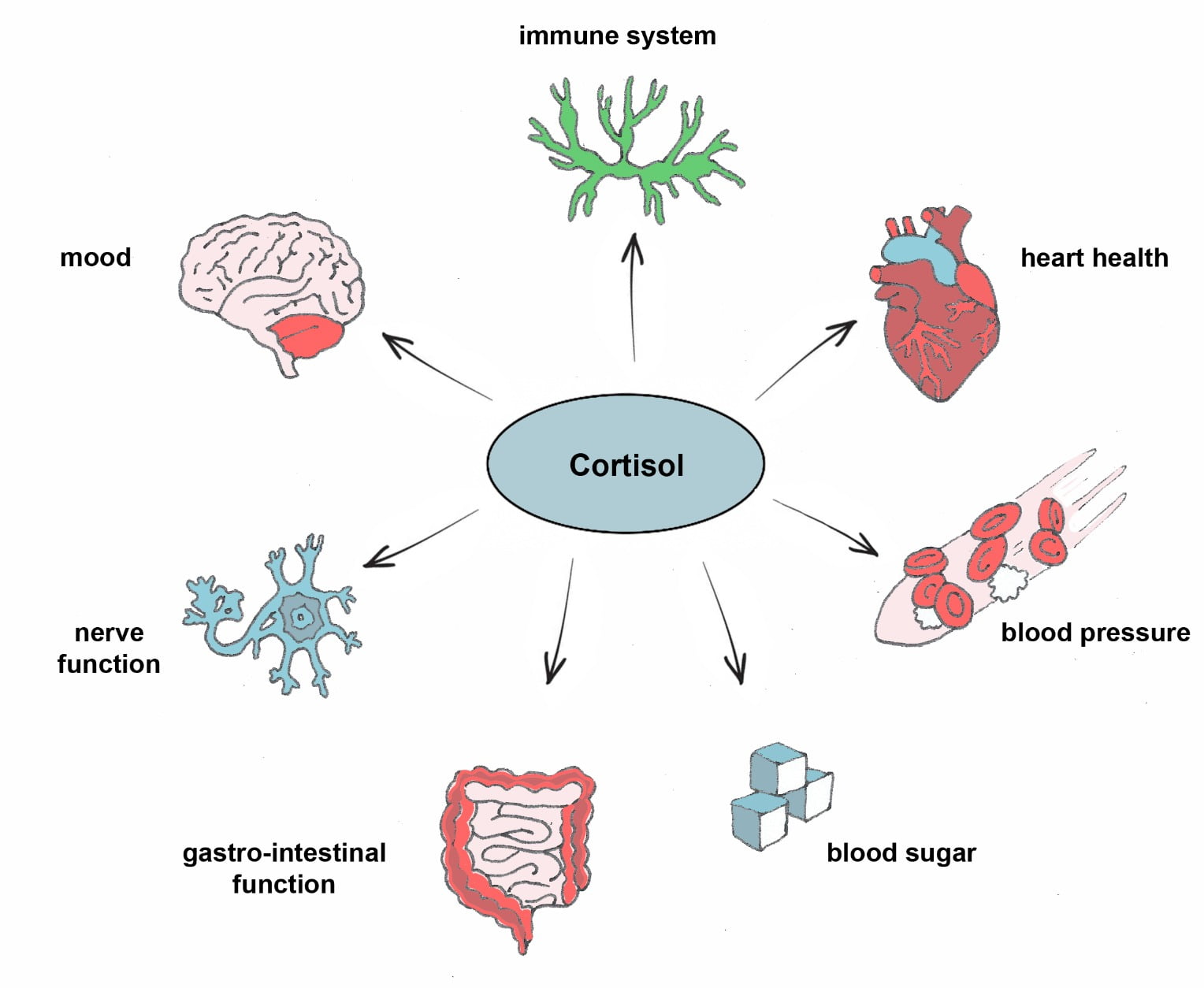
Activity can help regulate our heart and breathing rate, body temperature and emotions, reduce pain (gammo-aminobutyric acid production) and lay down new neural pathways.
Movement to music helps the brain’s motor and somatic cortices communicate movement messages to the body
more efficiently.
This assists in regulating the smooth flow of movement.
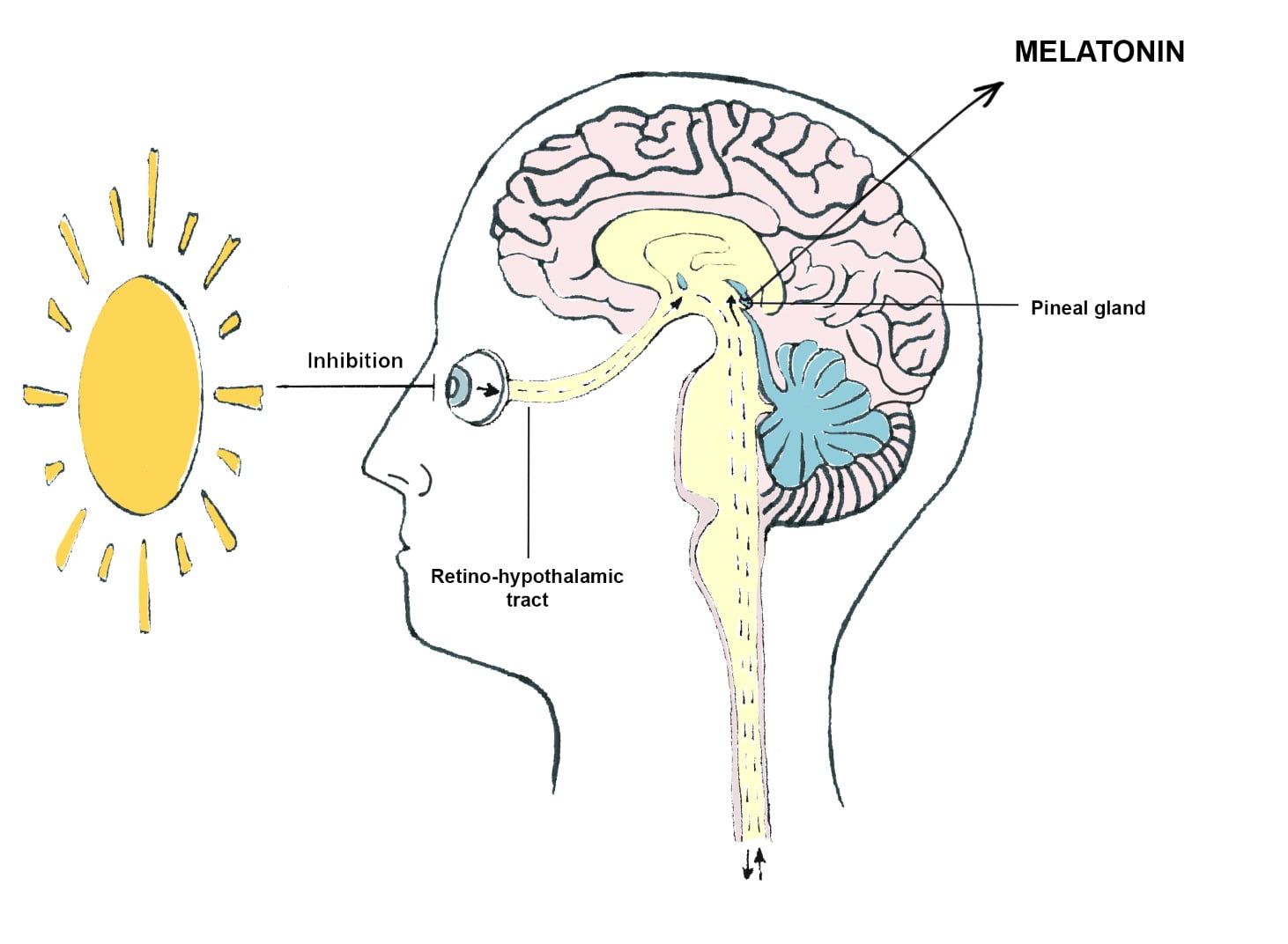
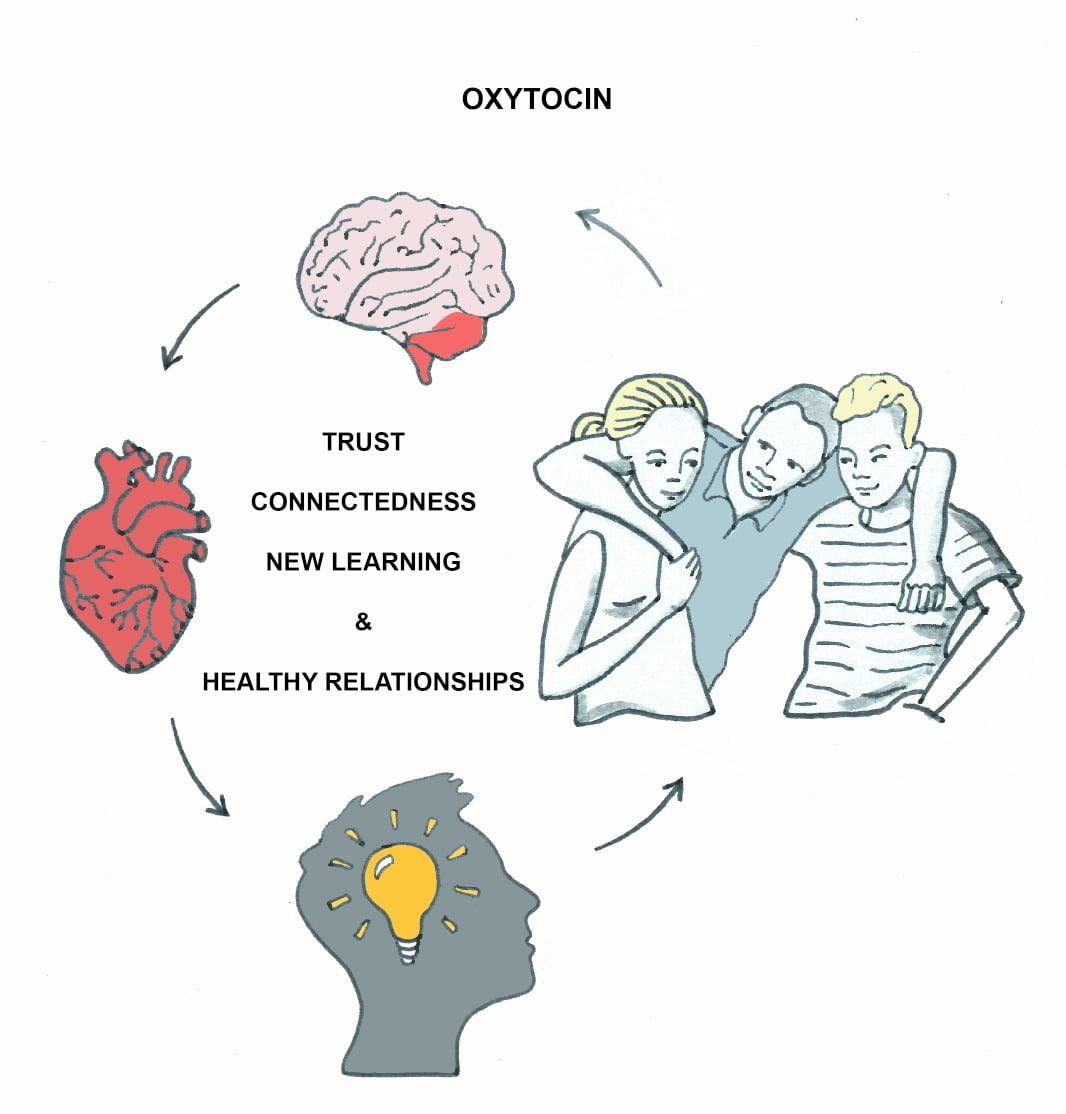

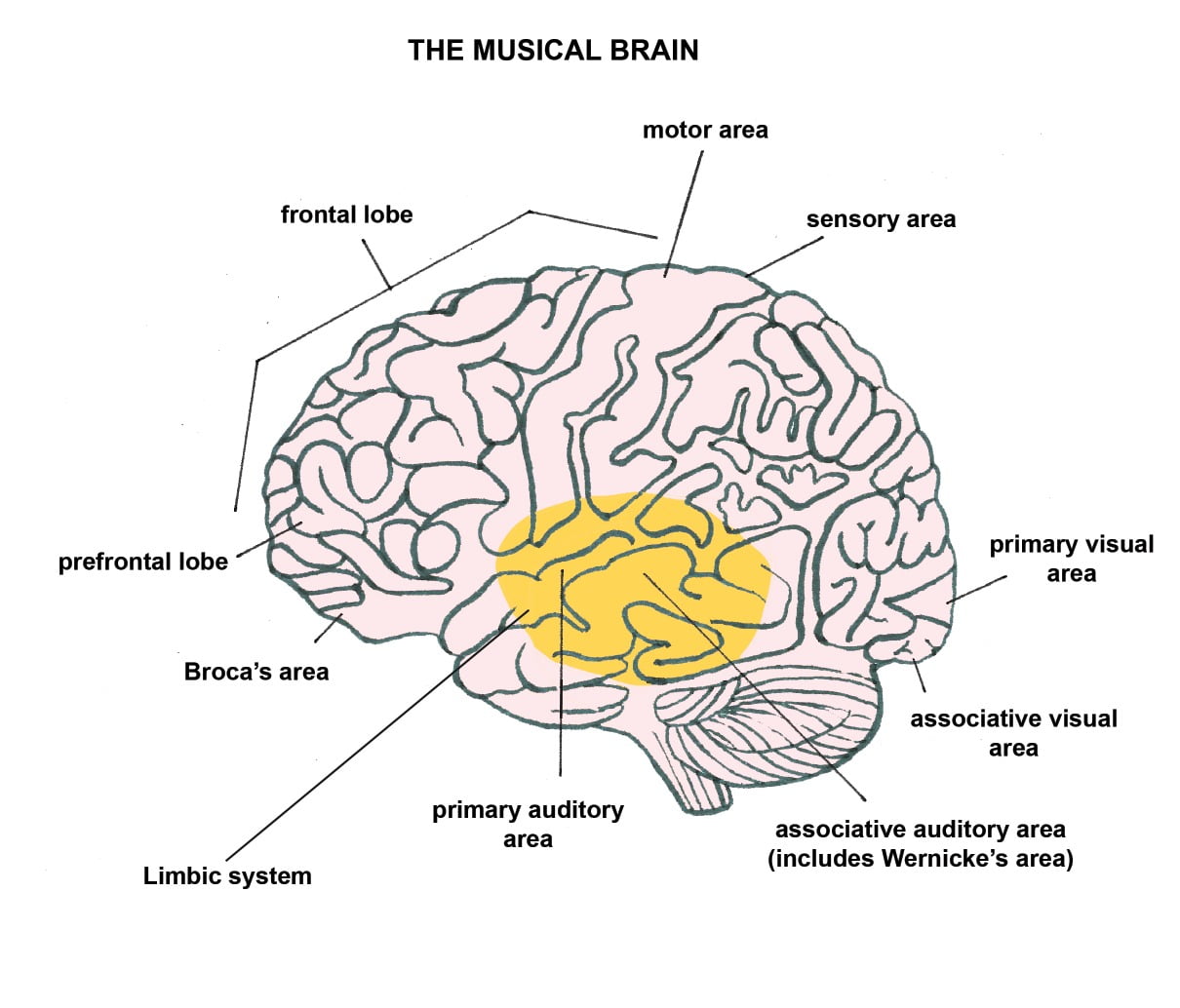
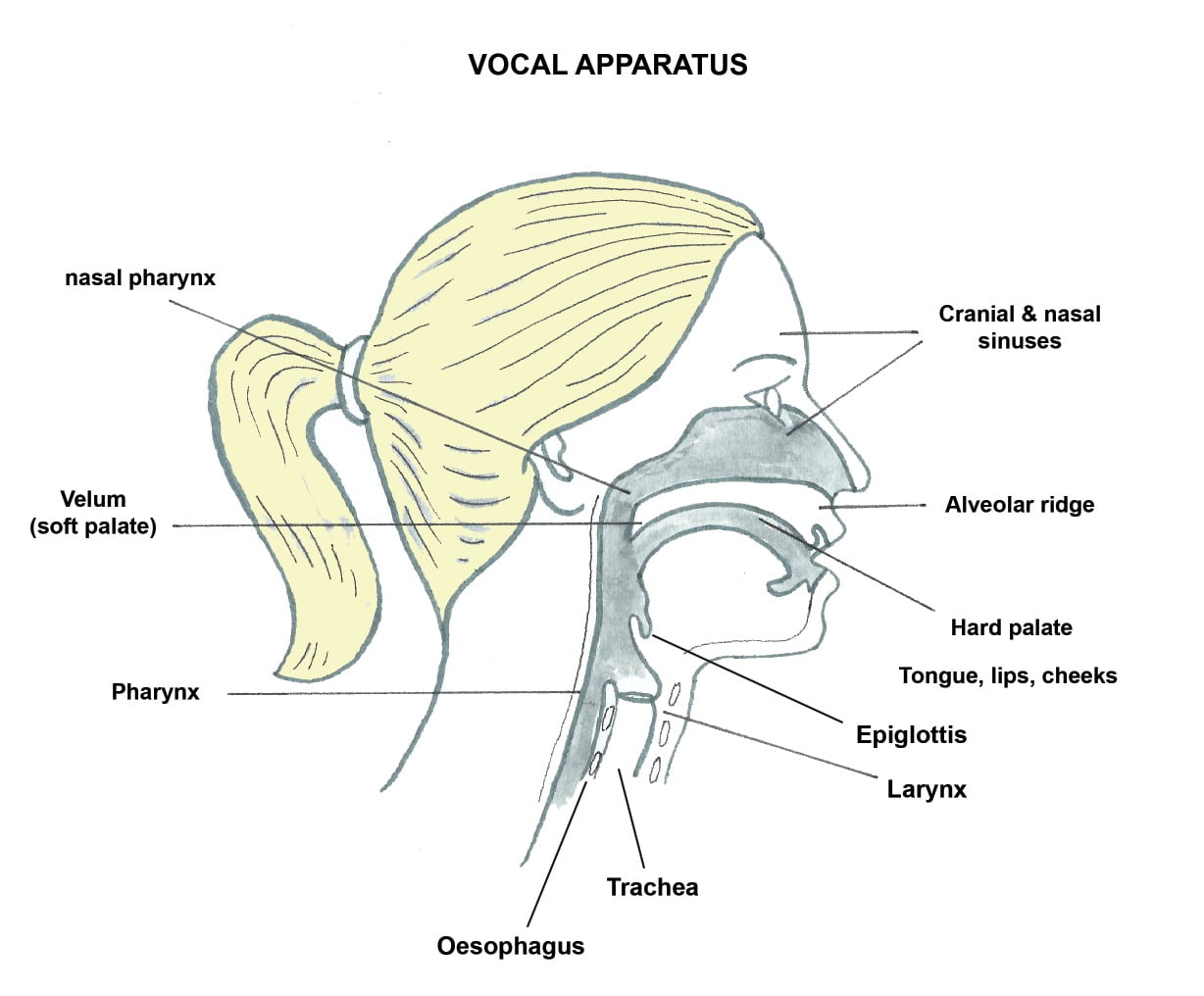
A scoping review of the evidence on the role of the arts in improving health and well-being by the World Health
Organization: 9789289054553-eng.pdf
All-Party Parliamentary Group on Arts, Health and Wellbeing Inquiry Report on Arts for Health and Wellbeing:
Creative_Health_Inquiry_Report_2017_-_Second_Edition.pdf (culturehealthandwellbeing.org.uk)
Evaluation report on harnessing music to improve our health, wellbeing and communities by Music for Dementia: Power-of-Music-Report-Final-Pages.pdf (exactdn.com)
Frühholz S, Trost W, Grandjean D. The role of the medial temporal limbic system in processing emotions in voice and music. Prog
Neurobiol. 2014 Dec;123:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Oct 5. PMID: 25291405.
Irons, Y., Sheffield, D., Ballington, F. & Stewart, D. (2019) A systematic review on the effects of group singing on persistent pain in people
with long‐term health conditions. European Journal of Pain, 24:71–90.
Kleber, B. & Zarate, M. (2014) The Neuroscience of Singing. In Welch, G., Howard, D.& Nix. J. The Oxford Handbook of Singing: Oxford
University Press
Kreutz, G., Bongard, S., Rohrmann, S., Hodapp, V. and Grebe, D. (2004) ‘Effects of Choir Singing or Listening on Secretory
Immunoglobulin A, Cortisol, and Emotional State’, Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 27 (6), pp. 623-635
Kumar, A, Tims, F., Cruess, D., Mintzer, M., Ironson, G., Loewenstein, D., et al. (1999). ‘Music therapy increases serum melatonin levels
in patients with Alzheimer’s disease’, Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, 5(6), pp. 49-57
Skingley, A., & Bungay, H. (2010) The Silver Song Club Project: Singing to promote the health of older people. British Journal of
Community Nursing, 15, 3, 135-40
Skingley, A., Martin, A., & Clift, S. (2015) The contribution of community singing groups to the well-being of older people: Participant
perspectives from the UK. Journal of Applied Gerontology, available online pre-publication, 1-23
Vickhoff, B., Malmgren, H., Åström, R. et al. (2013) Music structure determines heart rate variability of singers
Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00334
Wydenbach, N & Vella-Burrows, T. (2020) Singing for People with Parkinson’s. Devon, UK: Compton Publishing.





























Music4Wellbeing is a Kent-based charity that specialises in therapeutic musical interventions to improve wellbeing.
UK Registered Charity number 1205413.
© 2024 Music4Wellbeing. All rights reserved.

Thank you for your interest in supporting us! Music4Wellbeing is a Registered Charity and any donations are gratefully received.
All donations are directly invested into improving our facilities and expanding our programme of events.
If you would like to make a donation via bank transfer, our bank details are:
Account Name: Music4Wellbeing
Sort Code: 60-83-01
Account Number: 20497460
Thank you again!
Turn your daily shopping into every day magic! easyfundraising partners with over 7,500 brands who will donate part of what you spend to your cause at no extra cost
Brands pay us a commission because when you start your shop from the easyfundraising website or app, they can see we sent you to them. If you make a purchase, a commission is generated, and we turn that into a donation – magic!